Use case
Automating On-Demand Developer Environments for Preview and Testing
- Lakshya Chhajed
About the Customer
The customer is a global funding and trading company that provides trading services for financial markets. Their platform offers opportunities for traders to get funded by showcasing their skills in real-time market environments. The firm supports a diverse range of trading strategies across various instruments, with no minimum deposit requirements and a profit-sharing structure that can reach up to 100%. They aim to empower traders by providing them with the capital needed to succeed while fostering a supportive community for continuous learning and growth. The program features an evaluation and growth model, allowing traders to start with a real money account from day one and progress based on their performance.
Customer Challenge
The customer faced challenges in enabling developers to test their features or bug fixes without disrupting other ongoing work. Their current testing process in a shared staging environment caused contention, as it was not isolated. This created delays and inefficiencies, as changes could potentially affect other team members.
The lack of dedicated environments for developers also increased the risk of errors in production. Developers needed an independent way to verify their changes efficiently. Addressing these issues was critical for improving the development process and maintaining the quality of software deployments.
Solution
The solution involved implementing automated, on-demand environments using AWS services. This project was completed in three phases, leveraging infrastructure-as-code and automation tools to streamline development and testing workflows.
Phase 1: Preparation and Planning:
Key Requirements:
- Environment Isolation: Used AWS Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS) namespaces for developer-specific environments.
- Automation: Automated the creation, deployment, and teardown of environments with Helm charts.
- Monitoring and Logging: Integrated centralized monitoring using Grafana dashboards with namespace filtering.
- Resource Optimization: Employed EC2 t3.large (spot) instances for cost efficiency, coupled with Karpenter to manage scaling and stopping idle resources.
- Governance Foundations:
- Role-based access model: Adopted IAM Identity Center (or IAM + SSO) groups mapped to GitHub OIDC-assumed roles:
- DevOpsMaintainerRole (pipelines, Helm, rollback)
- PlatformAdminRole (cluster & account).
- Least-privilege pipelines: GitHub Actions uses OIDC -> STS to assume a short-lived role per repository; policies restrict to the required AWS APIs (ECR, S3, ALB, CloudFront, ElastiCache).
- Role-based access model: Adopted IAM Identity Center (or IAM + SSO) groups mapped to GitHub OIDC-assumed roles:
Phase 2: Pipeline Implementation and Deployment
Two pipelines were developed to automate environment management:
- Environment Provisioning Pipeline:
- Accepted developer inputs such as branch names.
- Built and deployed applications using Helm charts.
- Configured AWS resources, including Application Load Balancers (ALB), ElasticCache, and CloudFront, to provide isolated testing environments.
- Governance checks in CI/CD:
- Change control: Every code and infra change requires PR + 2 approvals; merges stamp the artifact SHA and plan ID into the deployment record.
- Environment Teardown Pipeline:
- Scheduled automation to stop idle environments during nights and weekends.
- Released EC2 resources and notified developers of the shutdown status via Slack.
Phase 3: Post-Deployment Monitoring and Validation
- Established monitoring dashboards in Grafana.
- Validated load balancer configurations and Kubernetes resource metrics.
- Ensured efficient resource release through teardown automation.
- Detective controls: (AWS Config)
- Required tagging enforcement
- EBS and S3 encryption compliance
- IAM policy wildcard restrictions
- All findings into Security Hub (with GuardDuty/Detective integration)
- Data Protection:
- Strict no-production-data policy in preview/non-prod environments
- Data masking pipelines for sensitive datasets
- S3 buckets secured with KMS encryption, bucket-owner-full-control, and block-public-access
- Enforced TLS-only communication
- Private connectivity via VPC Endpoints with restrictive endpoint policies
- EKS workloads isolated using namespace-level Network Policies and dedicated Security Groups per pod
Phase 4: Cost Optimization Strategy
To ensure cost efficiency while maintaining developer agility, a dynamic cost-optimization workflow was implemented. The approach focused on automation, idle resource detection, and developer-controlled lifecycle management.
- Smart Restart Workflow:
- Developers can instantly restart their environments on demand by triggering a GitHub workflow (/start-developer<branch>). The workflow resumes previously stopped resources within minutes, restoring the same configuration and data state.
- Financial Impact:
- Idle Hours Savings: By scheduling nightly and weekend shutdowns, overall EC2 and EKS costs were reduced by approximately 45–55% during non-working hours.
- Resource Right-Sizing: The use of Spot Instances and automated node scaling further reduced compute costs by an additional 20–25%, without compromising performance.
- Total Reduction: Combined automation measures achieved a total cost reduction of nearly 65–70% in developer environment operations.
- Continuous Optimization
- The cost-optimization workflow is continuously improved through AWS Cost Anomaly Detection and CloudWatch metrics, enabling proactive responses to cost spikes and ensuring sustained operational efficiency.
Below is the flow diagram illustrating the architecture of the implemented solution:
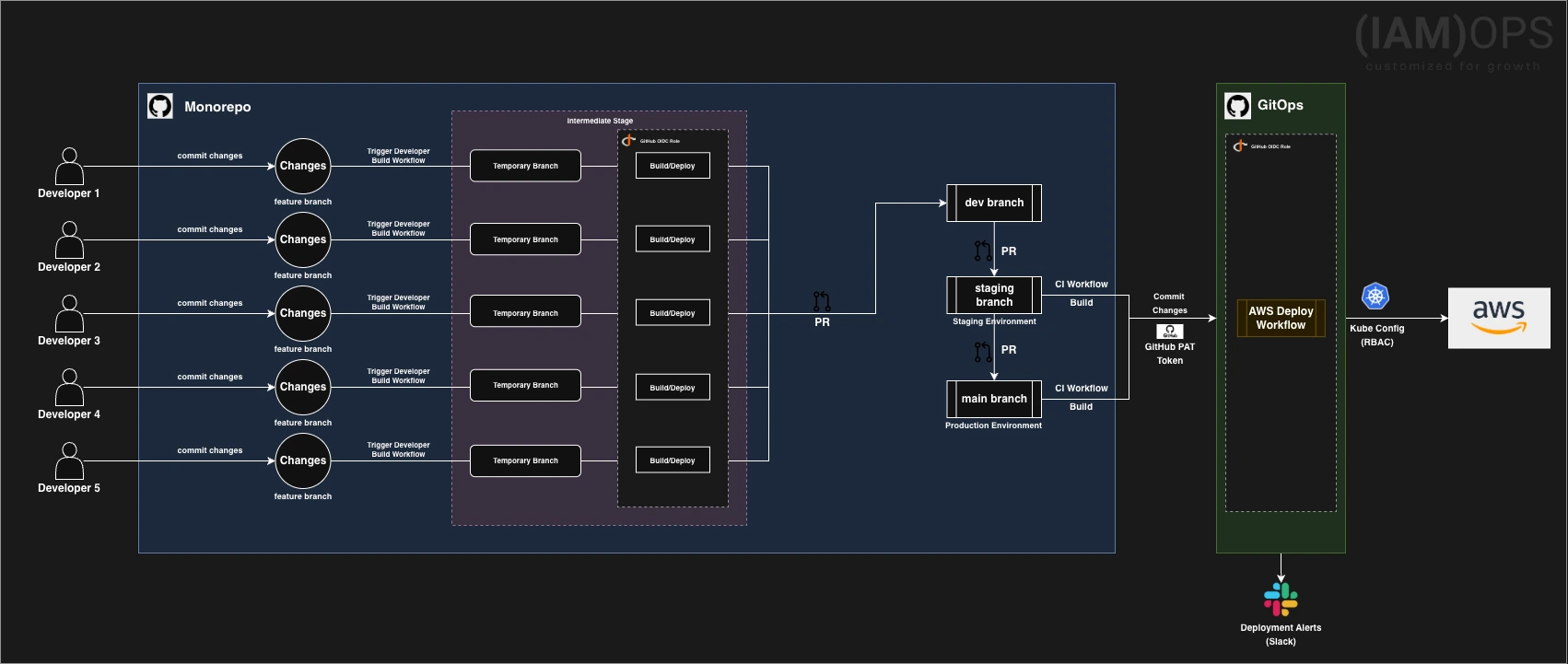
Results & Benefits
The implemented solution delivered significant improvements in efficiency, cost savings, and developer productivity:
- Automated Developer Environments:
- Reduced manual effort for provisioning and managing environments.
- Enabled faster feedback cycles with provisioning completed in minutes.
- Optimized Resource Usage:
- Idle environments were automatically stopped, reducing cloud costs during non-active periods.
- Enhanced Collaboration:
- Isolated environments prevented resource contention and improved team collaboration.
- Governance & Compliance Outcomes:
- 100% auditable environment lifecycle (PR→Plan→Apply→Teardown) with Git evidence.
- Consistent tagging enables cost/showback and chargeback for preview usage.
- Separation of policies via role boundaries and short-lived credentials.
- Operational Efficiency:
- Automation reduced manual intervention and allowed quicker testing cycles.
- Cost Optimization:
- Efficient resource allocation ensured cost savings during low-activity periods.
- Security Enhancements:
- Role-based access control provided secure namespace isolation.
- Comprehensive logging ensured traceability.
About IAMOPS
IAMOPS specializes in providing cloud-based DevOps solutions with a focus on AWS, Azure, and GCP. With expertise in automation, cloud-native infrastructure, and CI/CD pipelines, IAMOPS helps organizations optimize their cloud operations, ensuring efficiency, security, and scalability. IAMOPS holds multiple AWS Specializations and is committed to delivering innovative solutions that meet the unique needs of its clients.


